The main types of LEDs are miniature, high power devices and custom designs such as alphanumeric or multi-color.
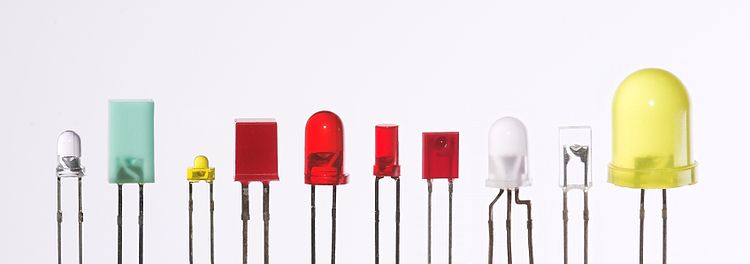
LEDs are produced in a variety of shapes and sizes. The color of the plastic lens is often the same as the actual color of light emitted, but not always. For instance, purple plastic is often used for infrared LEDs, and most blue devices have clear housings. Modern high power LEDs such as those used for lighting and backlighting are generally found in surface-mount technology (SMT) packages, (not shown).
Miniature
These are mostly single-die LEDs used as indicators, and they come in various sizes from 2 mm to 8 mm, through-hole and surface mount packages. They usually do not use a separate heat sink. Typical current ratings ranges from around 1 mA to above 20 mA. The small size sets a natural upper boundary on power consumption due to heat caused by the high current density and need for a heat sink.

Different sized LEDs. 8 mm, 5 mm and 3 mm, with a wooden match-stick for scale
Common package shapes include round, with a domed or flat top, rectangular with a flat top (as used in bar-graph displays), and triangular or square with a flat top. The encapsulation may also be clear or tinted to improve contrast and viewing angle.
There are three main categories of miniature single die LEDs:
- Low-current — typically rated for 2 mA at around 2 V (approximately 4 mW consumption).
- Standard — 20 mA LEDs at around 2 V (approximately 40 mW) for red, orange, yellow, and green, and 20 mA at 4–5 V (approximately 100 mW) for blue, violet, and white.
- Ultra-high-output — 20 mA at approximately 2 V or 4–5 V, designed for viewing in direct sunlight.
Five- and twelve-volt LEDs are ordinary miniature LEDs that incorporate a suitable series resistor for direct connection to a 5 V or 12 V supply.
Medium-power LEDs are often through-hole-mounted and used when an output of a few lumen is needed. They sometimes have the diode mounted to four leads (two cathode leads, two anode leads) for better heat conduction and carry an integrated lens. An example of this is the Superflux package, from Philips Lumileds. These LEDs are most commonly used in light panels, emergency lighting, and automotive tail-lights. Due to the larger amount of metal in the LED, they are able to handle higher currents (around 100 mA). The higher current allows for the higher light output required for tail-lights and emergency lighting.
High-power
High-power LEDs (HPLED) can be driven at currents from hundreds of mA to more than an ampere, compared with the tens of mA for other LEDs. Some can emit over a thousand lumens. Since overheating is destructive, the HPLEDs must be mounted on a heat sink to allow for heat dissipation. If the heat from a HPLED is not removed, the device will fail in seconds. One HPLED can often replace an incandescent bulb in a flashlight, or be set in an array to form a powerful LED lamp.
Some well-known HPLEDs in this category are the Lumileds Rebel Led, Osram Opto Semiconductors Golden Dragon, and Cree X-lamp. As of September 2009, some HPLEDs manufactured by Cree Inc. now exceed 105 lm/W (e.g. the XLamp XP-G LED chip emitting Cool White light) and are being sold in lamps intended to replace incandescent, halogen, and even fluorescent lights, as LEDs grow more cost competitive.

LEDs have been developed by Seoul Semiconductor that can operate on AC power without the need for a DC converter. For each half-cycle, part of the LED emits light and part is dark, and this is reversed during the next half-cycle. The efficacy of this type of HPLED is typically 40 lm/W.A large number of LED elements in series may be able to operate directly from line voltage. In 2009, Seoul Semiconductor released a high DC voltage LED capable of being driven from AC power with a simple controlling circuit. The low-power dissipation of these LEDs affords them more flexibility than the original AC LED design.





