Speech by the Chairman of the Autonomous Region
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region is situated in the northwestern part of China. With beautiful landscapes, rich resources and great potential for development, it is China's important reserve of strategic resources. Bordering on 8 countries and having 17 opened national ports, it is a gate and hub for China to open to the west. Since ancient times, Xinjiang has been an important hub for oriental-occidental trade and friendly exchanges, and a controlling section of the world famous Silk Road. Now it is a controlling section of the second Eurasia Railway.
Since New China was founded in 1949, in particular since the policy of reform and opening up was adopted, the people of Xinjiang, relying on rich resources and favorable geographic position, made full use of international and domestic resources and markets, unswervingly tried to turn abundant resources into economic strength and adhered to the policies for promoting economic and trade growth. As a result, the opening of Xinjiang has reached a new high and its investment environment improved greatly. The strategy of western development continued to be implemented. Xinjiang has entered a new stage of development in which Xinjiang people are building a well-off and harmonious socialist society in an all-round way. So a bright prospect and boundless business opportunities presented themselves for the development of Xinjiang.
Xinjiang is a beautiful golden land endowed with abundant resources. We sincerely welcome friends at home and abroad to Xinjiang for mutual benefit and development and for a better future!
I. Survey
(i) Geographic Location
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, also called Xin for short, is situated in the northwestern border area of China. In southeast, it neighbors Gansu Province, Qinghai Province and the Tibet Autonomous Region. Geographically, Xinjiang is located in 73 º 40' -96 º 23' east longitude and 34 º 25' -49°10' north latitude. It is 2,000 km long from its eastern border to the western border and 1,650 km long from its south border to the northern border. It covers an area of 1.6649 million square kilometers, accounting for one sixth of Chinese territory. So Xinjiang is China's largest administrative region at the provincial level.
Xinjiang is in the hinterland of the Eurasian Continent. The Asian geographic center lies close to the city of Urumqi. From northeast to southwest, Xinjiang borders Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. With a borderline of 5,600 km, it is one of China's provinces with the longest borderline. In ancient times, Xinjiang was an important section of the Silk Road. In modern times, it serves as a gate and passageway for China opening to the west.
Under the government of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region there are 5 autonomous prefectures, 7 prefectures, 2 cities at the prefecture level, 20 cities at the county level, 62 counties and 6 autonomous counties. 33 counties (cities) are in border areas.
Characteristic of Xinjiang landform can be described as mountains and basins alternating with each other and basins caught in mountains' embrace. Local people simply describe this characteristic as "three mountains with a basin between each Two". In the north lies Altai Mountains, in the south is Kunlun Mountains, while Tianshan Mountains lay along the middle dividing Xinjiang into two parts: in the southern part stretches Tarim Basin and in the northern part Jungar Basin. By custom, the part south of Tianshan Mountains is called South Xinjiang, the area north of Tianshan Mountains called North Xinjiang. Tarim Basin, the largest of its kind in China, lies between Tianshan Mountains and Kunlun Mountains. In the center part of Tarim Basin
stretches Taklimakan Desert, covering an area of 330,000 square kilometers, the largest mobile desert in China and the second largest in the world. 2,100-km-long Tarim River is the longest continental river in China. In east Xinjiang is Turpan Basin where the lowest point is -154m high, being the lowest part of China in height above sea level.
(ii) Climate
In climate, Xinjiang is under the control of a typical temperate continental climate, featuring long sunshine time, high cumulative temperature, wide diurnal amplitude and long frost-free period. With the annual precipitation of 188 mm, Xinjiang is a region with the least rainfall in China. The local annual mean air temperature stands at 10.4 ºC , with the average air temperature in the coldest month (January) ranging from -14℃ to -20 ºC and that in the hottest month (July) varying between 25-32 ºC. The mean sunshine time is 2827.6 hours. In mountains of Xinjiang, there are many rivers resulting from snow broth on mountains. Oases lie on the edges of basins and in river valleys. With oasis taking up 5% of its total area, Xinjiang is characterized by oasis eco-system.
(iii) Population and Ethnic Groups
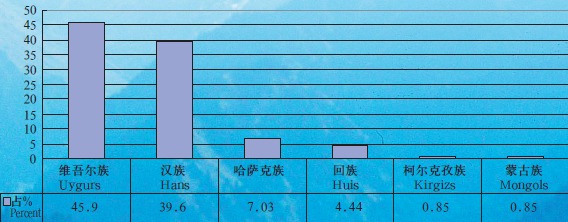
In 2005, Xinjiang had a population of 20.1 million, with urban population making up 37.2% and rural population 62.8%. Ethnic people account for 60.4% of the total. Xinjiang is inhabited by 47 ethnic groups, 13 of which are native. In the population, Uygurs make up 45.9%, Hans 39.6%, Kazaks 7.03%, Huis 4.44%, Kirgizs 0.85% and Mongols 0.85%. In Xinjiang, there live 44,000 Tajik people, 41,500 Xibo people, 24,600 Manchus, 15,100 Uzbeks, 11,200 Russians, 6,500 Dahurs, 4,700 Tartars and 113,700 people of other ethnic groups.
Percentage of Major Ethnic Groups in Population of Xinjiang
(iv) Infrastructure, Communications and Transportation
Aviation
Airport. Xinjiang has 12 civil airports, including 2 major international airports in Urumqi and Kashgar, and other airports in Yining, Altai, Tacheng, Karamay, Hotan, Arksu and Korla. 92 air routes have been opened, with Urumqi at the center, reaching all parts of Xinjiang, connecting Xinjiang to 62 major cities in China, and to 19 cities of 15 countries in Central Asia, the Middle East and Russia, linking Urumqi with 12 prefectures, autonomous prefectures and cities in Xinjiang. The total length of civil air routes has come to 119,500 km. With such many airports and so long air routes, Xinjiang has become a region of China with the most airports and the longest air route. In 2005, 3.39 million people travel by air and 30,000 tons of goods were transported by air.
Highway
Centering on Urumqi, a network of highways has been shaped, with 7 national highways as the backbone, connecting Xinjiang to Gansu, Qinghai and Tibet, and to as far as Central and West Asian countries. The network of highways connects 68 provincial highways, every city, county and town in Xinjiang. By 2005, the length of highways open to traffic in Xinjiang reached 89,531 km, of which 1,200 km are expressways. 4 expressways (Turpan- Urumqi-Dahuangshan Expressway, Urumqi- Kuytun Expressway, Kuytun-Sayram Expressway, the Hoxud-Korla Expressway) have been built and opened to traffic. So far, highway transport business has been conducted between Xinjiang and 5 foreign countries including Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikstan and Pakistan. 63 international highway transport lines have been opened in Xinjiang. All of these rank Xinjiang the top in China in terms of foreign transport lines, length of highways open to traffic and number of vehicles.
Railway
A network of railways has been formed, with Urumqi at the center. The length of railways has reached 2,925 km. In September 1990, the Lanzhou-Xinjiang Railway was extended to Alatav Pass Port (also called Alashankou Port), forming a second Eurasia railway. With completion of construction, Alatav Pass Port had become a major gate of China for opening to the west. Passenger trains have been run from Urumqi to Beijing, Shanghai, Chongqing, Zhengzhou, Chengdu, Ji'nan, Lanzhou, Hankou, Lianyungang, as well as from Kuytun to Xi'an, from Korla to Xi'an. International passenger trains run between Xinjiang and Kazakhstan.
Oil and Gas Pipelines
The West-East Gas Transmission Pipeline, more than 4,000 km long, has been completed, passing through 10 provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities. An investment of over RMB 120 billion yuan was made in this project which was designed to transmit 12 billion cubic meters of gas a year. Also completed were Karamay-Dushanzi Pipeline (double line), Karamay-Urumqi (double line), Lunnan-Korla Pipeline, Shanshan-Urumqi Pipeline and Urumqi-Lanzhou Pipeline. The first phase of Sino-Kazakhstan oil pipeline project has been put into business operation, being able to transmit 10 million tons of oil a year. By 2005, the total length of pipelines in Xinjiang had mounted to 3,003 km, carrying 22 million tons of oil and gas a year.
Banking and Insurance
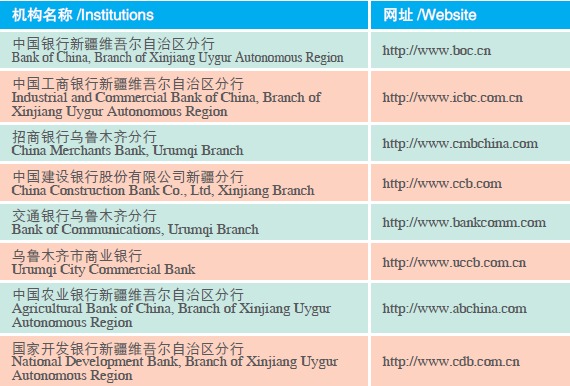
At the end 2005, 558 banking institutions operated in Xinjiang, with 2,767 business offices and 50,900 employees. At the end of 2005, the balance of deposits in banking institutions reached RMB 342.748 billion yuan. The year of 2005 saw operation of 11 insurance companies in Xinjiang, with 384 business offices. The premiums collected by these insurance companies stood at RMB 7.25 billion yuan in 2005.
Banking and Insurance Institutions in Xinjiang

Telecommunication
Xinjiang boasts long-distance digital transmission network, program control telephone network, mobile phone network, meeting video telephone network, digital data network, language information network, all of which formed modern communication networks linking Xinjiang with other parts of China. The optical cables are 28,915 km in total length. The number of fixed telephone subscribers reached 6.12 million, and that of mobile phone subscribers came to 5.31 million. Its telephone penetration rate stands at 57.6 phones per 100 persons.
Internet
Tianshannet, website of Xinjiang government, new Silk Road net and other nets and websites were built. All nets and websites have access to Internet through optical cables, wideband and digital broadcasting. The e-government is making steady headway. 15 prefectures, autonomous prefectures (cities), 13 departments of Xinjiang government and 26 counties have built their own public information websites. The number of subscribers of Internet has increased to 1.06 million.
(v) Foreign Exchanges
Friendly States and Cities
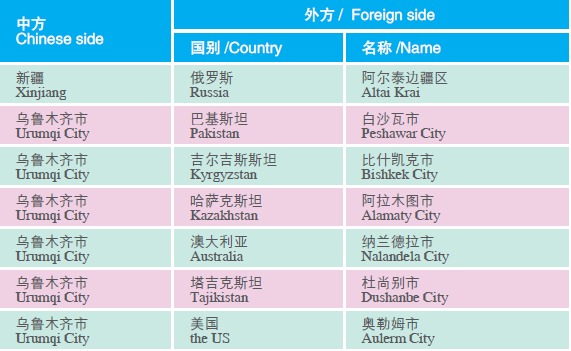
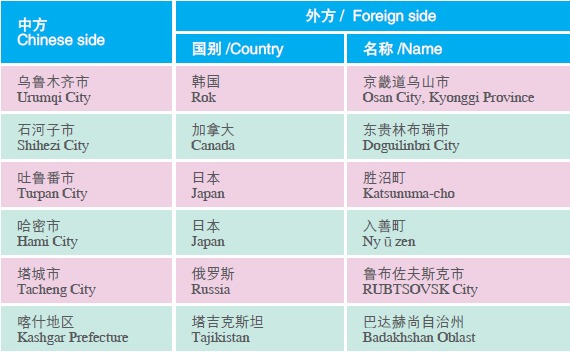
By the end of 2005, 13 prefectures and cities in Xinjiang had established friendly relations with states (cities) of 10 countries including Russia, Kazakhstan and the United States, greatly promoting the opening up of Xinjiang to the outside world.
Friendly and Cooperative Relations of Xinjiang with Foreign States (Cities)
Foreign-related Fairs
1. Urumqi Foreign Economic Relations and Trade Fair, also called Urumqi Fair for short, is the largest of its kind in western China. With the approval by the Ministry of Commerce of China, Urumqi Fair is held every year. Since 1992, Urumqi Fair has been held successfully for 15 times. Aimed at promoting trade and bilateral investment between China and Central and West Asian countries, it is a showcase to learn about Central, West and South Asia as well as Russia. Time: 1-5 September every year. place: Urumqi City
2. Central and West Asia Commodities Fair Kashgar, Xinjiang, China. The fair is also called Kargash Fair. The purpose of the Fair is to set up a platform for economic and trade cooperation of China with Central and West Asian countries, attract more businesses to Kashgar for opening international markets and enhance economic cooperation of Kashgar, Xinjiang and even of China with surrounding countries. Since 2005, Kashgar Fair has been held successfully for two times. Time: May-June, every year. Place: Kashgar City, Xinjiang.
(vi) Higher Education and Scientific Research
Higher Education
A multi-level and multi-discipline system of higher education with Xinjiang characteristics has been shaped by and large. At the end of 2005, there were 31 general institutions of higher learning. Xinjiang University is a national key university. The institutions of higher learning have a student population of 188,700 (75,000 are students of ethnic minorities) and 6,938 postgraduates. 1.7174 million students are studying at secondary vocational schools.
Scientific Research
At the end of 2005, 445,000 specialized technical personnel and 3 academicians of the Chinese Academy of Engineering worked in different fields in Xinjiang. There are 122 independent research and development institutions in Xinjiang. 6,545 major achievements have been made in scientific and technological research, 137 of which won national awards. Science and technology play an important role in economic development and social progress.
(vii) Tourism
Scenic Spots and Places of Historical Interest
There are abundant tourist resources in Xinjiang. China has 68 categories of tourist resources, and Xinjiang is endowed with 56 of them, ranking Xinjiang the top in all provinces and regions of China. Well-known are such place of scenic interests as Heavenly Lake, Kanas Lake, Bosteng Lake, Sayram Lake and Bayinbluk Grassland. Besides, there are many well-known places of historical interest, such as the remains of Jiaohe Ancient City, remains of Gaochang Ancient City, ruins of Loulan and Kezil Thousand-Buddha Grottoes. 28 natural reserves have been built in Xinjiang, 8 (Kanas, Tomur Mount, West Tianshan Mountain, Tarim Hu Poplar, Bayanbuluk Swan Lake, Ganjiasuosuolin, Lop Nur Wild Camel and Altun Natural Reserve) of which are national ones. Natural reserves cover a total area of 218,300 sq. km, accounting for 13.1% of the total area of Xinjiang. The project to build 8 ecological model zones has been approved, covering an area of 127,600 sq. km. There are 2 national ecological preservation zones in Xinjiang, covering area of 180,900 sq. km.

Golden tour routes: tourists may go on an eco-tour to the area around Kanas Lake, two scenic spots with Bosteng Lake and Heavenly Lake at the center respectively, a place of historical interests with Turpan as the focus, a folk-custom tourist attraction with Kashgar at the center and a beautiful tourist destination in Ili. You may have sightseeing by three tour routes: the Turpan-Korla-Kuqa-Taklimakan-Hotan-Kashgar route, the route of Urumqi-Heavenly Lake- Karamay-Ulungur Lake-Kanas Lake and the route of Urumqi-Kuytun-Qarma-Narat- Bayanbluk-Golden Beach (Jinshatan)-Urumqi.

Kanas Lake is the core of the national Kanas Natural Reserve. The water surface of the Lake is 1,375 meters above sea level. Looking like a crescent, the lake is 24.5 km, 1.9 km on the average and 188.4 meters deep at the maximum. It is one of China's deep lakes, covers an area of 69,000 mu and has a water-storage capacity of 4 billion cubic meters. Around the Lake is thick theropencedrymion which integrates itself with the boundless mountain grassland. Kanas Lake is a rare area in China that boasts European ecological system. In this protection zone, there live 798 varieties of plants, including 30 rare varieties, 39 varieties of animals, 117 varieties of birds and 7 varieties of fishes. Of these animals, 5 varieties are under Grade I protection by the State and 13 varieties under Grade II protection by the State. There are also 9 varieties of other rare animals and 60 new varieties of insects and fungus.

Heaven Lake (Tianchi Lake) is located north of Bogda Mountain, 110 km from Urumqi City. The surface of the Lake is over 1,900 meters above sea level. From south to north, it is more than 3,000 meters long and 1,500-odd meters wide from east to west. In good times, the lake surface is 4.9 sq. km in area, and it is 105 meters in maximum depth and can store 160 million cubic meters. This lake is a world-famous alpine lake. In 1982, it was listed in one of first group of national key scenic areas in China. Beginning from its entry, Heaven Lake scenic area can be largely divided into 4 natural landscapes: lower mountain belt, mountain boreal forest belt, alpine and subalpine belt, glacier and snow belt.
The Ancient City of Jiaohe lies at Yar Town, 13 km west of Turpan City. In the Western Han Dynasty, Jiaohe served as the capital of Anterior Cheshi, one of 36 states in the Western Regions. In the Tang Dynasty, the Western Regions Frontier, the highest military organ of the Tang Dynasty in the Western Regions, was once stationed here. The Ancient City is just like a large castle with strong defense. The defense in the city is very solid. A lot of relics were unearthed in the Ancient City of Jiaohe, like Lotus Eaves Tile and Lotus Buddhist Scripture of the Tang Dynasty.
Narat Grassland Narat Grassland lies on the south Xinjiang-north Xinjiang traffic artery. It is a home of meadow vegetation and one of the world's four. Since ancient times, it has been a famous pasture. Here, you can see plain and wide river valleys, high mountains, deep canyons, thick forest and vast grassland. Local custom and folkway of Kazak people are fresh and alien to tourists. Therefore, it is an ideal tourist attraction.
Local Food
Mutton kebab has become a nationwide popular food in China. Roast lamb is a famous delicacy of Xinjiang. Pilaf (steamed rice with muttons) and hand grabbed boiled mutton are favorite food of ethnic people. Nang, roast stuffed bun, hand-pulled noodles, oil fried wheaten food, steamed twisted roll, milk tea are traditional foods of local ethnic minorities in Xinjiang.
Related Articles:
Doing Business in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China: Economy
Doing Business in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China: Investment
Doing Business in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China: Development Zones





