In 2010, China's total expenditures on science and technology (S&T) continued to maintain a rapid growth. The expenditures of research and development (R&D) funds have increased steadily, the input intensity reached the highest level in the history.
I. Research and Experimental Development (R & D) expenditures
In 2010, national total R&D expenditures reached 706.26 billion yuan, jumping 126.05 billion yuan year-on-year, up by 21.7 percent, and with 1.76 percent of input intensity which higher than 1.70 percent in previous year. The average R&D expenditure per capita by R&D personnel (full-time work) was 277 thousand yuan, 23 thousand yuan more than that in the previous year.
In terms of different types of activities, the expenditure on basic research hit 32.45 billion yuan, increased 20.1 percent year-on-year; the expenditure on applied research stood at 89.38 billion yuan, increased 22.3 percent; the expenditure on experimental development totaled 584.43 billion yuan, climbing 21.7 percent. The proportion of expenditure on basic research and applied research which represents the original research was 17.2 percent, remained stable for three consecutive years.
In terms of different executive departments, the expenditures by all types of enterprises reached 518.55 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 22.1 percent; the expenditures by research institutions subordinated to the government departments arrived at 118.64 billion yuan, grew 19.1 percent; the expenditures by universities amounted for 59.73 billion yuan, climbing 27.6 percent. The proportion of expenditures among enterprises, subordinated to the government departments, and universities was 73.4, 16.8, and 8.5 percent respectively.
In terms of different industrial sectors*, the proportion of special equipment manufacturing stood at 2.04 percent, there are 4 sectors having input intensity exceeded 1.5-2.0 percent in R&D funding, 1.82 percent for pharmaceutical manufacturing, 1.59 percent for general equipment manufacturing, 1.59 percent for electrical machinery and equipment manufacturing, 1.50 percent for instrumentation, and cultural, office machinery manufacturing.
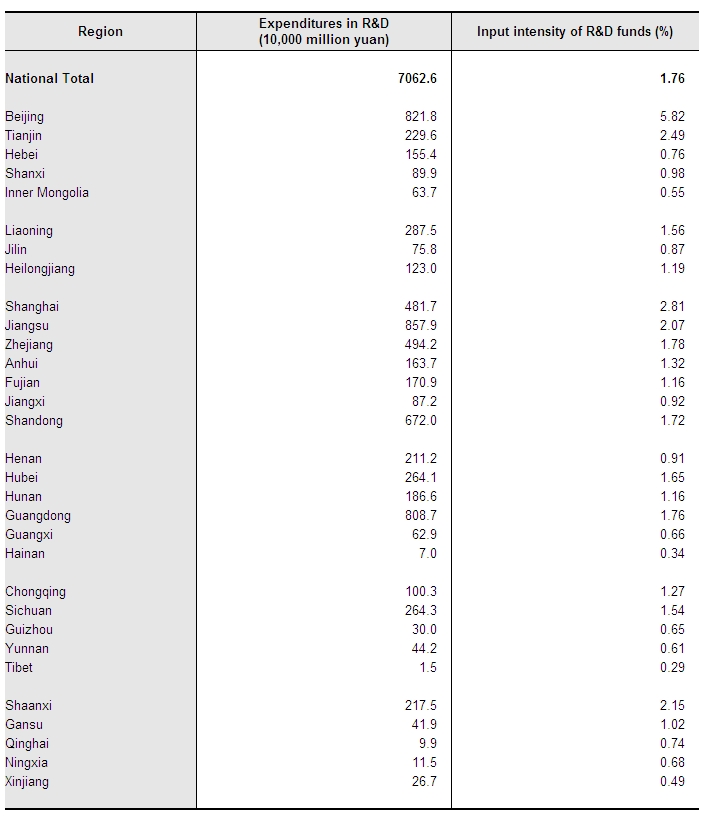
In terms of different regions, there were 6 provinces and municipalities with R&D expenditures more than 30 billion yuan; they are Jiangsu, Beijing, Guangdong, Shandong, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. The total expenditures of the above 6 provinces and municipalities reached at 413.65 billion yuan, accounting for 58.6 percent to national total expenditures. There were 7 provinces and municipalities with R&D expenditures intensity at or above national average level: Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Shaanxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Guangdong.
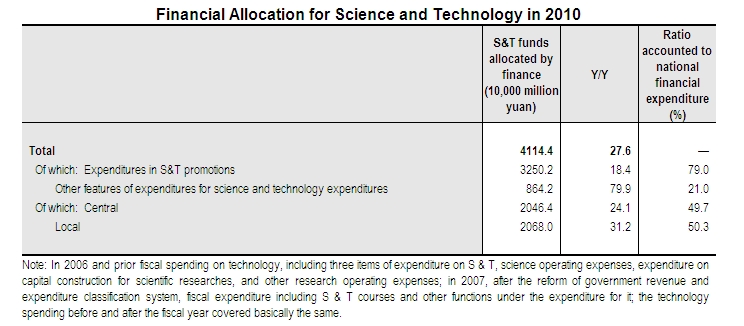
II. S&T funds allocated by finance
In 2010, S&T funds allocated by national finance amounted to 411.44 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 88.95 billion yuan, and rose 27.6 percent, sharing 4.58 percent to national financial expenditure.
Appendix: Expenditures in R&D by Region in 2010
Note:
1.Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Expenditures on R&D: refers to the actual expenditures spent in basic researches, applied researches and experimental development by executive units within statistical year. Including personnel fees, material costs, purchasing and construction fees of fixed assets, management fees and other expenses that actually spent in R&D activities.
Basic Research: refers to empirical or theoretical research aiming at obtaining new knowledge on the fundamental principles regarding phenomena or observable facts to reveal the intrinsic nature and underlying laws and to acquire new discoveries or new theories. Basic research takes no specific or designated application as the aim of the research.
Applied Research: refers to creative research aiming at obtaining new knowledge on a specific objective or target. Purpose of the applied research is to identify the possible uses of results from basic research, or to explore new (fundamental) methods or new approaches.
Experiments and Development: refer to systematic activities aiming at using the knowledge from basic and applied researches or from practical experience to develop new products, materials and equipment, to establish new production process, systems and services, or to make substantial improvement on the existing products, process or services.
2. Statistical Coverage:
R&D expenditure is covered all enterprises and institutions who has R&D activities in the whole of society, including industrial enterprises, research institutions subordinated to the government departments, universities, and enterprises and institutions in the industries with relatively intensive R&D activities (including agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fishery, construction, transportation, storage and postal industries, information transmission, computer services and software industry, finance, rent and business services, scientific research, technical services and geological prospecting, water conservancy, environment, and public facilities management industry, health, social security and social welfare, culture, sports and entertainment, etc.).
3. Data Collection:
Expenditure on R&D: medium-large sized industrial enterprises, research institutions subordinated to the government departments, and universities adopted comprehensive survey, small-sized industrial enterprises, and enterprises in other industries adopted comprehensive methods such as complete investigation, major investigation, and make use of estimate method to achieve R&D funds by using the Second National R & D resources inventory data.
*Industrial sector only includes data from medium and large-sized industrial enterprises.





