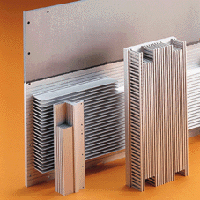
In electronic systems, a heat sink is a passive heat exchanger component that cools a device by dissipating heat into the surrounding air. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool central processing units or graphics processors. Heat sinks are used with high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronic devices such as lasers and light emitting diodes (LEDs), wherever the heat dissipation ability of the basic device package is insufficient to control its temperature.
A heat sink is designed to increase the surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Approach air velocity, choice of material, fin (or other protrusion) design and surface treatment are some of the factors which affect the thermal performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the eventual die temperature of the integrated circuit. Thermal adhesive or thermal grease fills the air gap between the heat sink and device to improve its thermal performance. Theoretical, experimental and numerical methods can be used to determine a heat sink's thermal performance.
Heat Sink Selection and Mechanical Criteria
| | Heat sink selection, taking into account mechanical conditions and requirements other than thermal criteria, is also decisive for the long-term reliable function of devices, modules or systems. It no longer suffices to restrict heat sink selection to dimensions such as length, width and height. It is equally important for quality assessment purposes, to understand the correlation that decisively influences the overall quality in the design and planning phase. |
| Heat sinks made of aluminium alloy as extrusion profiles (extruded sections) are partly subject to other criteria than those applicable to pressure die-cast parts or bent metal parts and other conditions must be taken into account during machining. It is therefore often necessary to take this criteria of considerable importance into account during the development phase. In the total concept of a device, the heat sink is a part that must match different components. It is therefore important during design to take into account that deviations from the nominal dimensions, i.e. tolerances, can be considerable during extrusion. An extruded section is produced by a heated aluminium block, the extrusion billet, being pushed through a tool, the die, with negative shaping of the contour to be produced . The high deformation forces that occur require correspondingly high section tolerances, so that considerable effort is necessary to minimise these tolerances.【More】 | |
Different Cooling Methods for Industrial Electronics
| In recent times, there have been many innovations in the semiconductor industry, and important developments have taken place, especially in the field of power semiconductors and IGBT technology. The higher power rating and the improved efficiency are particularly remarkable. These developments, however, have not affected the size of the components which still have a compact design. For the user, the combination of high efficiency and small space requirement is very desirable. However, the electronics engineer has to deal with the problem of how to dissipate the large amount of waste heat. This problem has to be solved by the manufacturers of cooling elements. It is up to them to develop and propose suitable methods.【More】 |
Know more about Heat Sinks:
SMT - Components and Heat Sinks
Written by Dora Men