Application
Until recently, the use of LEDs has been limited to electronic devices, ambient lighting, exterior lighting or for creating effects, because of the versatility of RGB LEDs and Controllers. With their low power consumption, LEDs are ideal for emergency lighting and have been used in this application for a number years.

As the development of White LEDs is progressing at an exponential rate, the performance of (LEDs), including efficiency, flux level, life, and the variation of colour, is advancing too, meaning we are now beginning to use them as direct light sources.
Example 1. LEDs are ideally suited to street lighting - accidents are scarce and there are few lamp changes, little maintenance, reduced energy use and low costs.
Example 2. LEDs are used as secondary light sources or in smaller rooms i.e. in lifts, railway carriages, corridors etc.
Advantages
The amazing potential of the LED is that it can offer high efficacy, ultra-long long life, instant start, good colour rendering, no UV, shock-proof, limited environmental impact…the list goes on. Additionally, because LEDs are based on Solid State technology, they can be controlled and programmed, making them the most versatile and flexible of light sources.
Disadvantages
White LEDs are still being developed to the point where they can be used as like-for-like replacements for their incandescent, fluorescent or HiD equivalent. Some of the chemicals used in the fluorescent crystals are recognised as hazardous. The main disadvantage would be low operating temperature for optimum life, efficacy and lumen maintenance. In terms of initial expenditure or capital outlay, LEDs are expensive but this argument can be countered over the life of the light source.
Key Properties
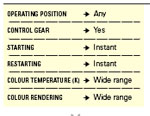
LED Modules
An LED module consists of several semiconductor crystals or single LEDs (semiconductor crystals with their housings) which are placed in series next to one another, or combined in some other form, on a conductor plate. The plate is not only a carrier but also makes possible the easy fixing of the LEDs and other optical, electronic or mechanical components.
The electrical layout of the conductor plate can be adapted to a particular application: as well as single operation, coloured LEDs can also be separately fixed using an appropriate layout so that plays of colour and sequences are possible within a module. Colours can be produced with an additive colour mixture because the LED module combines the three RGB colours (red, green, blue). The mixing of basic colours leads to the creation of every favourite tone or to various colour effects.





