Tokyo-based Mitsubishi Electric Corp has developed the MGFK47G3745 gallium nitride(GaN)high-electron-mobility transistor(HEMT)Ku-band(12–18GHz)amplifier for satellite earth stations.
Picture:Simplified schematic of amplifier.
Satellite-based communication,especially in the Ku-band,enables communication to be established under adverse conditions,such as during natural disasters,and in areas where communication facilities are hard to build.Mobile earth-based stations require in-vehicle portability and must be easy to install,so power-saving measures and downsized power transmitters are highly useful in helping to minimize the size of earth stations.
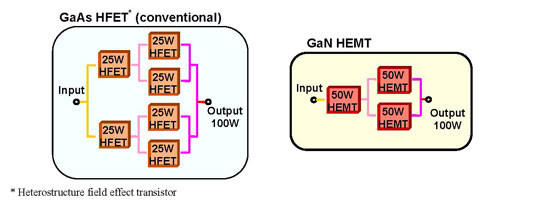
Mitsubishi Electric says that in recent years the use of gallium arsenide(GaAs)amplifiers in microwave power transmitters has increasingly been replaced with gallium nitride(GaN)amplifiers due to their high breakdown voltage,power density and saturated electron speeds.
Under operating conditions of 24V drain-to-source voltage(VDS)and 1A quiescent drain current(IDQ)and at frequencies of 13.75–14.5GHz,the new MGFK47G3745 features high typical output power at Pin=42dBm of 50W(47dBm),typical linear gain at Pin=27dBm(Glp)of 9dB(achieved with a new high-voltage gate structure and optimized layout),and typical power-added efficiency(PAE)at Pin=42dBm of 30%(10 points greater than the preceding model MGFK44A4045).
The internally impedance-matched device is expected to reduce the number of high-frequency amplifiers by half and contribute to greater power saving and downsizing for power transmitter equipment.
Samples of the new MGFK47G3745 will begin shipping on 1 October.Mitsubishi Electric adds that it expects to expand its lineup of Ku-band satellite earth stations in future.





