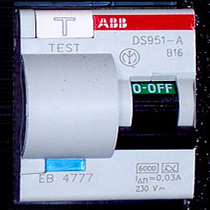
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit.
| | The circuit breaker is an absolutely essential device in the modern world, and one of the most important safety mechanisms in your home. Whenever electrical wiring in a building has too much current flowing through it, these simple machines cut the power until somebody can fix the problem. |
Without circuit breakers (or the alternative, fuses), household electricity would be impractical because of the potential for fires and other mayhem resulting from simple wiring problems and equipment failures.
Standard current ratings for Europe
International Standard--- IEC 60898-1 and European Standard EN 60898-1 define the rated current In of a circuit breaker for low voltage distribution applications as the maximum current that the breaker is designed to carry continuously (at an ambient air temperature of 30 °C).
| Type | Instantaneous tripping current |
| B | above 3 In up to and including 5 In |
| C | above 5 In up to and including 10 In |
| D | above 10 In up to and including 20 In |
| K | above 8 In up to and including 12 In For the protection of loads that cause frequent short duration (approximately 400 ms to 2 s) current peaks in normal operation |
| Z | above 2 In up to and including 3 In for periods in the order of tens of seconds. For the protection of loads such as semiconductor devices or measuring circuits using current transformers |
Types of circuit breakers
Many different classifications of circuit breakers can be made, based on their features such as voltage class, construction type, interrupting type, and structural features.
MORE:
Circuit Breaker Operation
Arc interruption
Short-circuit current
Written by Nicolas Yang