At the Optical Fiber Communication conference & exposition 2015 (OFC 2015) in Los Angeles, CA (22-26 March), Tokyo-based Mitsubishi Electric Corp is unveiling a distributed feedback (DFB) laser diode for 25Gbps fiber-optic communications in 100Gbps systems operating over a wide range of temperatures from -20°C to 85°C. Four DFB laser diodes can be mounted on 100Gbps high-speed communication transceivers in order to achieve lower power consumption and enhanced communication performance for increased efficiency in data centers. The new DFB laser diode should also help to simplify the requirements for transceiver design, says the firm.
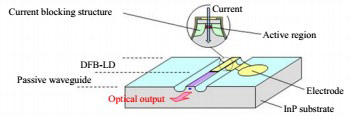 Fig.1 Schematic of DFB laser for 25Gbps fiber-optic communications.
Fig.1 Schematic of DFB laser for 25Gbps fiber-optic communications.
During atttempts to develop a DFB laser with high-speed response suited to 25Gbps operation, a current-blocking structure using semi-insulating semiconductors (doped with impurities to achieve high electrical resistance) showed promise. However, high output power was not possible due to poor current injection efficiency in the active region. In response, Mitsubishi Electric developed a new current-blocking structure using semi-insulating semiconductors that achieves low capacitance, yielding efficient current injection in the active region without degrading high-speed response. The current injection efficiency in the active region improved by 12% compared with firm's existing products. More than 10mW output power at 85°C is obtained.
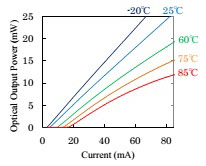 Fig.2 Current dependence of optical output power.
Fig.2 Current dependence of optical output power.
The transmitter optical sub-assembly (TOSA) for 100Gbps transmission includes 4-wavelength 25Gbps DFB lasers, whose high output power compensates for the optical loss caused by an optical multiplexer inside the TOSA.
Also, wide-ranging temperature operability eliminates the need for cooling, helping to reduce power consumption. This, together with a high-quality modulation waveform, helps to simplify 100G transmission system design. Due to having low capacitance and a short laser length (75% the length of the firm's existing products), the current-blocking structure enables what is claimed to be a high-quality modulation waveform with a mask margin of more than 20%. The high-quality modulation waveform simplifies laser-driving circuit design and hence communication transceiver design.
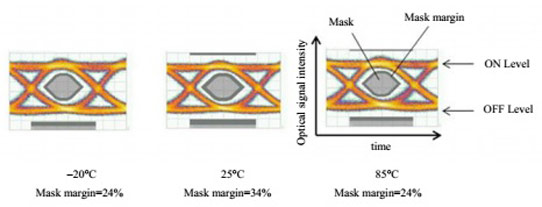
Fig.3 Modulation waveform
Mitsubishi Electric says that in future it will continue to develop DFB lasers with the aim of realizing wider-temperature-range operation and higher conversion efficiency from electric current to optical output power. This should contribute to high-density packaging and low power consumption in fibre-optic communications transceivers.





