Tokyo-based Mitsubishi Electric Corp has developed a gallium nitride high-electron-mobility transistor (GaN HEMT) offering high output power and efficiency for use in base transceiver stations (BTS) operating in the 3.5GHz band for fourth-generation (4G) mobile communication. Samples will be released from 1 April.
As a result of the deployment of long-term evolution (LTE) and LTE-Advanced mobile networks, demand is rising for base transceiver stations that can offer increased data volume, smaller size and lower power consumption, says the firm. In response, Mitsubishi Electric has developed samples of high-output, high-efficiency GaN HEMTs operating at a drain voltage (Vd) of 50V and frequencies of 3.4-3.8GHz for macro- and micro-cell BTS.
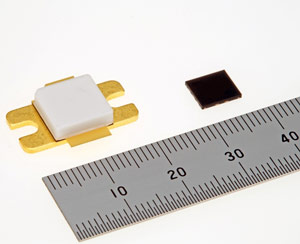
Picture: GaN HEMT for 3.5GHz-band 4G mobile communication BTS: the MGFS50G38FT1 (left) and MGFS39G38L2 (right).
Product features include what is claimed to be world-leading power output of 100W for macro-cell BTS (realized through transistor optimization), helping to expand BTS coverage range. Also, by adopting GaN HEMTs and transistor optimization, high efficiency helps to reduce BTS size and power consumption.
The 100W MGFS50G38FT1 device for macro-cell BTS and the 9W MGFS39G38L2 device for micro-cell BTS have saturated output powers of 50 dBm and 39dBm, respectively, as well as linear gains of 17dB and 19dB, and realize high drain efficiencies of 74% and 67% in load-pull measurements. High efficiency allows a simpler cooling system, contributing to reduced size and power consumption.





