A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically valves fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure.
| | The simplest, and very ancient, valve is simply a freely hinged flap which drops to obstruct fluid (gas or liquid) flow in one direction, but is pushed open by flow in the opposite direction. This is called a check valve, as it prevents or "checks" the flow in one direction. Valves are found in virtually every industrial process, including water & sewage processing, mining, power generation, processing of oil, gas & petroleum, food manufacturing, chemical & plastic manufacturing and many other fields. |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chinese Valve Manufacturers
The earliest Chinese valve manufacturer started in 1950’s, at that time, there were only several valve manufacturers and they belong to government. In 1980’s, after the the reform and opening-up policy, quite a few Chinese valve manufacturers founded, most of them are in Zigong and Wenzhou.
| | Now, there are hundreds of Chinese valve manufacturers with large capability. However, most of Chinese valve manufacturers are not recognized by international oil, gas and other industrial end user, as well as EPC contractors. They sold Chinese made valves by OEM for international valve brand, by earning little profit at cost of high pollution. With the increase of raw material and the depreciation of US dollar, the profit is becoming lower and lower, which leads Bankruptcy to some Chinse valve manufacturers. Chinese valve manufacturers need to attend international completion with reputation in name of their own brand. |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
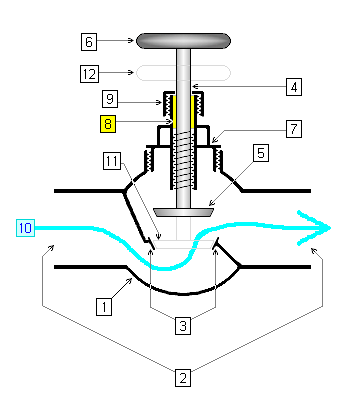
Components
The main parts of the most usual type of valve are the body and the bonnet. These two parts form the casing that holds the fluid going through the valve.
| Body The valve's body is the outer casing of most or all of the valve that contains the internal parts or trim. The bonnet is the part of the encasing through which the stem (see below) passes and that forms a guide and seal for the stem. Bonnet A bonnet acts as a cover on the valve body. It is commonly semi-permanently screwed into the valve body or bolted onto it.Many ball valves do not have bonnets since the valve body is put together in a different style. Ports Ports are passages that allow fluid to pass through the valve. Ports are obstructed by the valve member or disc to control flow. Valves most commonly have 2 ports, but may have as many as 20. Handle or actuator A handle is used to manually control a valve from outside the valve body. An actuator is a mechanism or device to automatically or remotely control a valve from outside the body. Disc A disc or valve member is a movable obstruction inside the stationary body that adjustably restricts flow through the valve. | |
| Cross-sectional diagram of an open globe valve. |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Applications
| | Valves vary widely in form and application. Sizes typically range from 0.1 mm to 60 cm. Special valves can have a diameter exceeding 5 meters. Valve costs range from simple inexpensive disposable valves to specialized valves which cost thousands of US dollars per inch of the diameter of the valve. Disposable valves may be found in common household items including mini-pump dispensers and aerosol cans. |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Types
Valves are quite diverse and may be classified into a number of basic types. Valves may also be classified by how they are actuated: Hydraulic, Pneumatic, Manual, Solenoid, Motor.
General types: 1.Ball 2.Butter-Fly 3.Gate 4.Globe 5.Needle 6.Plug 7.Spherical 8.Fixed Cone 9.Non-Return (Check) Valve.
| | | | | |
| Hastelloy ball valve | steel swing check valve | Inconel gate valve | Cast iron butterfly valve | globe valve |
| | | | | |
| needle valve | Plug valve | Spherical valve | Fixed Cone valve | check valve springs |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Valve operating positions
| | Valve positions are operating conditions determined by the position of the disc or rotor in the valve. Some valves are made to be operated in a gradual change between two or more positions. Return valves and non-return valves allow fluid to move in 2 or 1 directions respectively. |
References: wikipedia
Written by Nicolas Yang